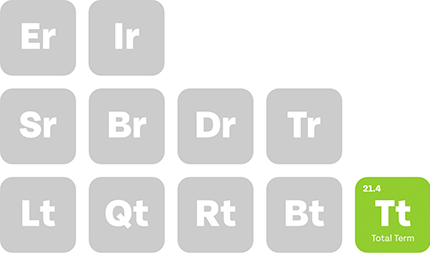
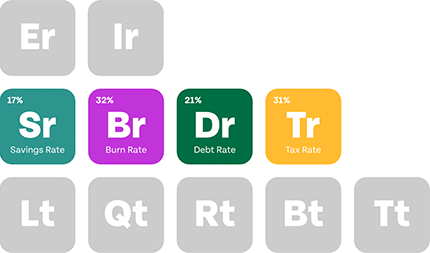
When you think of an ophthalmologist, you may imagine a highly skilled doctor performing sensitive eye surgeries or diagnosing complicated vision problems. You probably don’t think about the differences between ophthalmologist private practice and hospital employment. Yet where an ophthalmologist chooses to work can significantly impact income, autonomy, and career satisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Ophthalmologist private practice typically offers higher earning potential than hospital employment.
- Working for a hospital can provide security and less administrative work, with less earning potential.
- Private practice has higher overhead and greater responsibility than hospital-based physicians.
- Contract review, insurance, and investment strategies can help optimize income in both careers.
Table of Contents
Ophthalmologist Private Practice vs Hospital Salary Comparison
Income for an ophthalmologist private practice varies widely, even within the same practice or hospital. In a private office setting, for instance, income can depend on patient volume, service offerings, and a doctor’s ability to charge higher fees. Income in these practices is usually higher for ophthalmologists who perform more specialized or in-demand procedures. Income also depends on how many procedures can be completed within a given timeframe. Some of the most lucrative services include cataract removal and replacement, LASIK surgery, and high-end lens implants.
Hospital staff positions, on the other hand, generally provide a set salary. While these positions offer the security of a predictable income, they have much lower earning potential. Ophthalmologist salaries for hospital staff positions have a median salary of $391,000, with most positions paying between $200,000 and $388,000 annually, depending on location, experience, and facility budget.
Why Ophthalmologist Private Practice Often Leads to Higher Income
One of the main advantages of private practice is the ability to control your earning potential. By setting their own fees, doctors can manipulate their schedules to accommodate more patients and add high-profit services to their practice offerings. Private practices also typically retain a higher percentage of revenue after expenses than hospitals do.
Ophthalmologist private practice owners, therefore, can often take home more income in an average year than their hospital-employed counterparts. It is not unusual to hear of practitioners in high-volume urban areas or markets with few competitors who make between $250,000 and $400,000 or more in annual take-home pay.
There are, of course, expenses to weigh against the potentially higher salary. Owning and operating a private practice also means higher overhead. Office space, equipment, staff salaries, and insurance all eat into revenue and can be expensive. Any slowdown in patient volume can directly affect the bottom line. A certain amount of business skill is also required to manage a practice effectively and remain on the cutting edge of both medical technology and service marketing.
Why Some Ophthalmologists Choose Hospitals Over Private Practice
Hospital positions may not always offer the highest salaries compared to a well-run private practice, but they also have their advantages. When you choose to work for a hospital, you have peace of mind when you arrive at work because you don’t have to worry about payroll, billing, or practice marketing. All of that is done by support staff so you can focus on patient care.
Hospital-employed ophthalmologists may also receive better benefits packages than they would on their own. Generous health insurance, retirement, paid continuing education, and even malpractice coverage are not unusual in hospital contracts. Hospitals can also be an attractive place to work if you want access to the latest medical equipment and research opportunities, as well as a team-based environment that values collaboration.
Balancing Ophthalmologist Private Practice Complexity with Hospital Stability
Choosing between private practice and hospital employment often comes down to weighing complexity versus stability. When you are self-employed, you are in the driver’s seat when it comes to income potential, but you are also captain of a ship with all of the responsibilities and risks involved. You make decisions about hiring staff and technology investments and are solely responsible for remaining compliant with healthcare laws.
The American Medical Association’s Private Practice Sustainability resources highlight how independent physicians can thrive by balancing business ownership with patient care, even amid changing healthcare systems.
Hospital employment, on the other hand, transfers much of that burden to the employer. For physicians who desire set work hours, less administrative complexity, and a predictable paycheck, this can be a welcome trade-off. The downsides are that you have much less control over your income ceiling. Your salary will be set by the hospital, and major raises are rare.
How Location Impacts Success in Ophthalmologist Private Practice and Hospital Work
The geographic location can also affect ophthalmologist salary in both practice and hospital environments. Urban environments tend to have larger patient bases and more procedures than suburban or rural areas, but competition may also be greater, especially in cities with a high density of physicians.
Rural or underserved areas may sometimes offer surprisingly competitive salaries as hospitals and clinics compete to recruit the best talent. Physicians who are willing to relocate to these areas may find additional incentives such as sign-on bonuses, student loan repayment assistance, and housing stipends.
Financial Planning Tips for Success in Ophthalmologist Private Practice
In any case, maximizing your ophthalmologist private practice income requires a high degree of financial planning and preparation. This includes everything from having your employment contracts reviewed to obtaining low-cost insurance and making smart investments. A well-negotiated contract, for example, can have a long-term effect on your salary, whether you join a hospital team or buy into a private practice.
Financial planning also helps protect against the unexpected. Owners of private practices need to budget for seasonal fluctuations in patient volume, unexpected equipment repairs, and sudden changes in reimbursement rates. Ophthalmologists in hospital settings may want to plan for their next career move, such as moving into an administrative position or teaching at a local university, which can also increase earnings over the long term.
Making the Right Career Choice: Ophthalmologist Private Practice or Hospital?
No matter which path you take, remember that your income is not entirely determined by your work environment. You can maximize your ophthalmologist salary by carefully considering the services you offer, the contracts you sign, the location where you work, and the financial strategies that you apply.
If you are ready to take the next step in protecting and preserving your income, or starting your own private practice, the expert team at Physicians Thrive can help. We specialize in contract negotiation and income optimization as well as long-term wealth strategies specifically for physicians, including disability insurance for self employed professionals. Contact us today to see how we can help you launch, grow, and maximize your success in your ophthalmologist private practice.